November 5th, 2013

We’ve mentioned before that you can’t ever be completely secure online. But, some actions you take make you more secure and significantly less likely to be hacked. Andy O’Donnell of About suggests a number of mistakes that are commonly made and how they can lead to hacking. Here’s a list of some of the most common, as well as how you can avoid making them.
- Not Using Unique Passwords
Why would you need more than one password for your online accounts? If you use a long, strong password that’s difficult to break, you should be safe, right? Actually, no. Not all accounts are compromised by a third party guessing or breaking your password. Sometimes, large lists of passwords are stolen from companies. If your password is the same on every site you have an account with, a criminal could now have access to all those sites, rather than just the one. If you’re worried about remembering all of those unique passwords, consider using a password manager.
- Using An Unsecured Wireless Network
Whether it’s at home or at the office, your wireless network needs to be secured to keep out intruders. First, make sure you’re using adequate encryption. Check your router’s settings and enable WPA2 based encryption, rather than the less secure WEP. Then, set a long, strong password using upper and lowercase letters, symbols and numbers. Try to avoid using things like pets’ or children’s names or birth dates because those are likely to be known, or able to be found out, by others.
If you receive an unsolicited email with an attachment, don’t download the attachment. It’s simple advice, but many users believe they can download the attachment to find out what it is. In actuality, they’re downloading malware, which immediately infects their system. The same goes with pop-ups. Even with a pop-up blocker active in your web browser, you may see pop-ups from time to time, especially if you’re on a questionable website. Clicking on these pop-ups will often start a malware download.
To be properly secured, you need an active antivirus program and a firewall in place. These have to be turned on to work. This seems obvious, but many users will disable them if their computer is running slow, or if they’re having trouble running another application. This is ill advised. Also, security software needs to be continuously updated. This is to enable to software to recognize the latest pieces of malware and viruses. If you fail to update your antivirus, it becomes less and less effective.
These common mistakes make you an attractive target for hackers. To improve your cyber security, or to fix the damage already done to a device by malware and viruses, call Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335.
November 4th, 2013
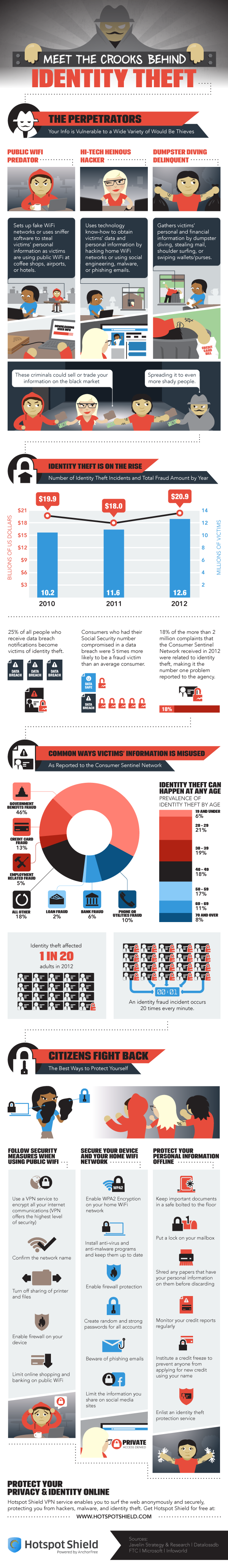
Protecting your computer from viruses and malware is only part of the concern of cyber security. Identity theft, which often begins with data being stolen over unsecure networks, through malware, or phishing scams, is also a costly threat.
Peter Nguyen, of the HotSpot Shield blog, writes that the number of identity thefts in the US is constantly growing. Last year, there were 12.6-million victims, which is enough for an identity theft to happen every 3-seconds. The financial loss of the victims totaled almost $21-billion.
The included infographic covers the how and why of identity theft. It also gives a few tips for how to stay safe. In addition to some offline measures, like shredding documents containing personal information, monitoring your credit reports, and locking your mailbox, here are the most important online safety tips.
- Beware public WiFi. When using an unsecured network at a coffee shop or other public place, limit your activity. Any transactions that require you to input financial information should wait. A firewall should be enabled on your device and you should turn off sharing of printers and files.
- Use proper security on your home wireless router. The router is your first line of defense, so make sure WPA2 encryption is enabled and a strong password is required to log on.
- Keep antivirus programs running in the background and keep them updated. Updating security software enables them to detect and protect against the latest threats.
- Keep social media profiles private. Every social network gives you options for what you share with whom. Make sure strangers don’t have access to information like your birthday, family information, phone number and employment history. This can all be used for identity fraud.
- Use long, strong passwords. Many security experts suggest passwords longer than 6-characters and using both upper and lowercase letters, numbers and symbols.
To improve the security of your devices at home, or at your business, call Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335. We not only fix devices, we also help keep them safe.
October 25th, 2013

Security vulnerabilities for wireless routers are extremely dangerous. For a typical user, it’s difficult to diagnose when your router has been hacked. Making matters worse is that many users don’t know how to update with new security patches, or don’t understand the risk of not having regularly updated firmware.
As Lucian Constantin, of ComputerWorld reports, these problems were clearly illustrated recently when a security researcher uncovered flaws in the security of some Netgear routers. The WNDR3700v4 model of Netgear’s N600 Dual-Band Gigabit Router let’s hackers bypass authentication when using the web based interface. When remote administration is turned on, the router’s settings and the user’s activity can be changed and monitored from anywhere.
There are numerous possibilities for criminals exploiting this security flaw. Traffic running through the router could be re-routed to malicious websites, internal network services could be exposed, and data transmitted through the router can be monitored and stolen.
Netgear faced a similar problem in July when the same vulnerability was discovered in the firmware of another model. They quickly released a patch, but have apparently failed to check other routers for the security flaw. Many users have also failed to take notice as one report notes about 73-percent of users with the vulnerable router have failed to update.
One security expert warns to never voluntarily turn on remote administration for any device. Not only does it expose you to the possibility of attacks, but it often contains bugs.
In order to protect your router, even if you aren’t using this particular Netgear model, is to use WPA2 protection and restrict access with a strong, unique password. Also, stay up to date with updates released by the manufacturer of your router.
For help improving the cyber security for any of your devices, at your home or business, call Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335.
October 22nd, 2013

Free public WiFi is a well known danger to your device’s security. These wireless networks are unsecured, which makes it easy for hackers to intercept data being transmitted over them.
Most companies also use a wireless network for their employees, which can be just as dangerous. It’s often overlooked, but, as Sam Narisi of IT Manager Daily reports, there have been a large number of exploits due to wireless routers having backdoors and holes in their security.
Recently, D-Link wireless routers were discovered to have a vulnerability that allows a third party to change the router’s settings without needing the password.
Security firm Independent Security Evaluators released a list of 13 wireless routers that they found to contain security flaws. The routers came from trusted companies like Belkin, Netgear and Linksys and allowed hackers to intercept information, gain access to computers on the network and bypass security.
A technique called “wardriving” has been used to crack wireless networks, as well. By simply driving around and area and searching for wireless signals, hackers are able to then use software to break the network’s encryption.
Internal wireless networks are not inherently secure. There are, however, steps you can take to improve their security. Installing the latest patches and continually updating the router’s firmware is important. Replacing your hardware regularly is also necessary since older devices will stop getting patches and have flaws the newer devices don’t. Use HTTPS for administrator connections. And of course, use a long and strong password on your router.
There are a number of ways a criminal can gain access to valuable data within your company’s network. In order to improve your entire security, call Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335.
October 21st, 2013

As we’ve mentioned before, it’s impossible to be completely secure. Hackers continually adjust their tactics and upgrade their tools to breach any network. Because of this constant evolution, security has to constantly change and be updated as well. Your security infrastructure becomes less effective every day. Debbie Mahler, of the State of Security blog, writes that security is a process. She suggests some tips for how to continually improve your cyber security.
- Identify the weakest link
In order to improve security, you first have to find out where it needs to be improved. Usually, employees are the downfall of any security infrastructure. Unsafe web surfing habits, or human error often result in breaches. It’s important to study their habits in order to put policies in place that will keep your business more secure.
Having a firewall in place, and password protection on routers is a great step towards being more secure. But, too many people fail to utilize the tools they have at their disposal. For example, there have been many instances of security breaches stemming from a failure to change default passwords on routers. If you’ve taken the time to put these measures in place, take the additional time to make sure you’re using them effectively.
This is a common IT security rule. For any file, no one should have access. That’s where you start, then add permissions as necessary. This will keep your most valuable data secure because only a select few will have access to it.
Catastrophic data breaches usually happen after your network has been infiltrated previously. And, each time there’s suspicious behavior on your network, the logs have the evidence. Be sure to regularly review the logs in order to catch potentially harmful situations before they explode into disasters.
Security for your business is a big job that requires constant supervision. For help, contact Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335. We offer security audits and solutions for any breaches in your current security infrastructure.
October 8th, 2013

Is your home WiFi network secure? Unfortunately, there’s a lot of bad information out there that convinces users that they’ve secured their home network, when in actuality it’s still as vulnerable as ever.
Eric Geier, of CIO, set out to debunk some popular myths regarding WiFi security in a recent article. The items on this list have been proven to be inconsequential for protecting you against potential threats.
You’ll find many individuals across the web suggesting you stop broadcasting your wireless router’s name, known as its SSID, or Service Set Identifier. This is to keep your network invisible from those you want to keep out. However, it will still be visible to most users and the SSID is easy to discover for hackers. Plus, trying to stay invisible can make you a target as criminals believe there may be valuable data on your network that you’re trying to conceal.
MAC stands for Media Access Control. A MAC address is an alphanumeric code used to uniquely identify each device on your network. You’re able to configure your router to only allow certain MAC addresses access to your network. In theory, this would keep out unwanted network users, even if they have your network’s password. However, hackers have tools to easily see the list of accepted MAC addresses and can then change their device’s address to match one of those. This makes MAC address filtering little more than a time waster.
In addition to the MAC address, each device on your network has a unique Internet Protocol, or IP, address. Your router issues an IP address to each device when they join the network. By changing configuration so your router only has a limited number of IP addresses to issue, you should be able to limit how many users your network can possibly have. Hackers are able to scan for IP addresses being used by your network, however. They can then assign an acceptable one to their device and by pass this security measure.
Another myth is that reducing the power of your wireless router will make it harder to be accessed by anyone outside your home. The theory is that since the WiFi network won’t be visible from as far away, not as many people will be able to penetrate it. Hackers use high-powered antennas, however. So, having a low powered router will only limit your use of your network.
If you’d like to truly secure your network, consider encryption and firewalls. Coupled with regularly updated antivirus software, this is the best way to keep your network and computer safe. For help improving the cyber security at your home or office, contact Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335.
September 30th, 2013

You’ve probably taken some precautions to make sure your computer is protected from malware, viruses and other potential security issues. But have you taken precautions to protect your router?
A recent post on NewsFactor notes that there are router-specific malware threats capable of reconfiguring it. A malware infected router is able to redirect users to malicious sites in order to steal data or infect them with more malware and viruses.
Imagine you are using your computer to check your bank balance. If your router is infected with malware, it could redirect you to a similar looking site that is actually designed to steal your log-in information. Minor differences will alert you that something is wrong, but you have to be looking for them. A slight difference in the way the site looks, or a missing option in the menu are tell-tale signs that this site isn’t legitimate.
Thankfully, most banking websites offer security specifically designed to alert you if you’re not on their official website. However, other websites don’t take the same precautions.
Your browser also has security tools available to help keep you safe in these situations. When the warning pops up that a website’s security certificate isn’t recognized, don’t ignore it. This is a warning that using this site puts your data at risk. If you see that warning, don’t use that website. If needed, contact the business directly by phone and ask them about their website.
To protect yourself, make sure your router is updated continuously. Newer models usually update automatically, but it’s worth checking to make sure. Also, use the password protection options. Not only should your router be password protected, but that password should be changed often and not easy to guess.
To find out how to improve the cyber security at your home or office, contact Geek Rescue at 918-369-4335.
July 31st, 2013

We’ve become so spoiled by regularly fast internet speeds that any load time we encounter is almost unbearable. Occasionally, even your fast, usually reliable internet connection becomes a slow frustration. Lifehacker has suggestions on what to check if you find yourself not-so-patiently waiting for websites to load.
If it’s not a sudden change, but rather a continuous problem that your internet is maddeningly slow, you may be getting what you pay for. Check with your provider for how fast the internet on your plan is, then use a site like speedtest.net to see if you’re getting the speeds you were promised.
If your connection is slower than it should be, try the tried and true method of turning off hardware then restarting. You can reset your modem, router and computer to try to fix the problem. You may discover that your wireless signal is too weak if you’re on WiFi. It could be as easy as moving your router to a different spot in the house, but there are a number of possible fixes to boost your signal.
Your internet speed can be significantly slowed down by programs or plug-ins that use a large amount of bandwidth. For example, if you’re using a download manager to download multiple large files, your speed in your browser is going to suffer. There are also tools that block elements on web pages that can use up your bandwidth, but that won’t speed up your connection, only help you get the most out of it.
It’s possible that the DNS server, which your computer uses to look-up websites, is having problems. There are ways to find the fastest DNS available, but if your DNS isn’t actually encountering issues, you won’t see much improvement.
In some cases, a slow internet is just the reality you have to deal with. If there are no easy fixes available, you can choose to load versions of websites with fewer design elements so they’ll load faster.
There are plenty of ways to try to maximize your internet speed, but sometimes it’s just time to find a new provider. Be sure to do your homework before making the switch so you know you’re getting the best option for you in your area.
To learn about all of your options in fixing a slow internet connection, consult the experts at Geek Rescue. Whether there’s a problem with your computer, router, modem or another source, Geek Rescue finds it and fixes it quickly. Come by or call us at 918-369-4335.


















